Familiarity with steam boiler or steam boiler
A boiler is an energy conversion or transmission system in which chemical energy from fuel is converted into thermal or electrical energy. It consists of a tank or a closed container in which liquids are stored and heated using hot gases from the combustion of fuels such as coal, fuel oil or natural gas burning in a furnace or from electric coils.
But first let us consider the term heat. Heat is vital in everyone's daily life. Whether it is the heat to warm the environment around us, or the heat to cook food, we all use it to some extent in our daily activities. Water and steam are very good carriers for heat and do not harm our environment. The boiling point of water at atmospheric pressure is 100°C or 212°F. By pressurizing the boiling system by sealing it, we can actually raise the boiling point. This is how pressure cookers work. An aeration vessel to increase the pressure to increase the boiling point. This makes the food cook in a much shorter time than when an open pot is used.
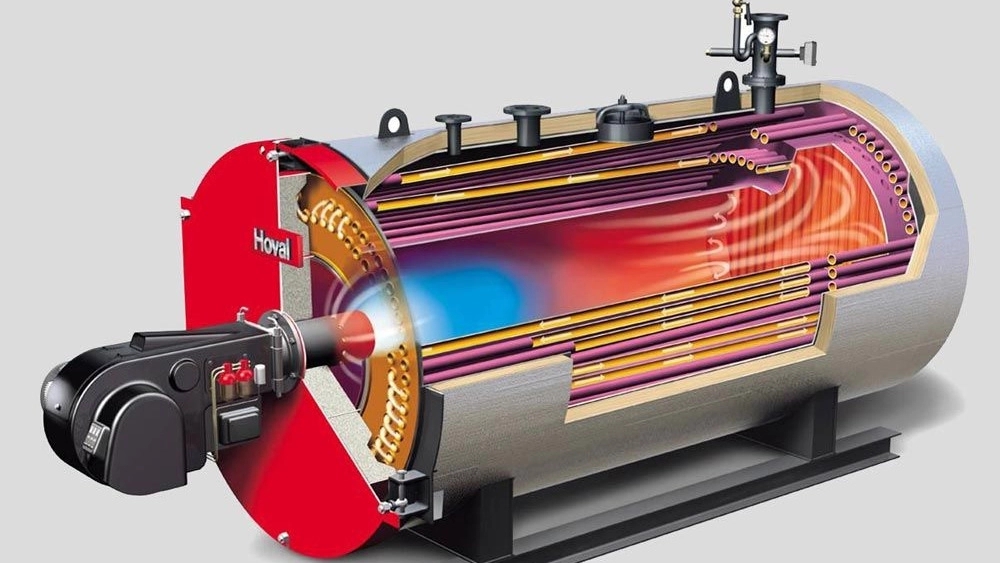
How does an industrial boiler work?
Industrial boilers can withstand much higher pressures than pressure cookers (domestic pressure cookers). Industrial boiler systems are often made by welding thick steel plates and create very high pressures. It must be super strong to deal with the high pressure, as failure to do so will result in forces close to exploding the bomb! The function of a steam boiler is to produce hot water or steam. Hot water boilers heat water for domestic or commercial heating and hot water supply. Steam boilers produce steam to drive turbines for provide electricity generation and other industrial heating applications.
To visualize the effects of steam generation using a boiler, think of steam powering a turbine. When steam passes through the blades of a turbine, the force turns the blades and accelerates the turbine. Steam contains a large amount of energy, so it makes the turbine very efficient and, depending on the fuel used to boil the water, Energy consumption is also very low.
The important components of the metal building of the boiler are:
Shell or body, which is an alloy steel cylinder with a thickness suitable for the working pressure of the boiler, and is made by rolling steel sheets and then welding
Furnace is also a steel cylinder. which is placed parallel inside the shell. Tube Plates are installed on both sides of the steel cylinder, inside which cutting or drilling is done based on the location of the smoke passage pipes and the furnace. done
The smoke tubes (Smoke Tube) which are made of alloy steel and are installed inside the steel cylinder of the boiler body parallel to the furnace and have the task of passing smoke and fire after the furnace.
base, chassis and connections (Skid & Connections) which are for holding the boiler and also for installing equipment on the boiler.
What are the different types of boilers?
There are different types of boilers for different types of applications. There are two main categories of boilers, each of which can be divided into several types:
Fire tube boiler - hot gas is used in several tubes to heat the surrounding water.
Water tube boiler - water tube It is heated by the surrounding hot gas.
Including how each of these methods are able to produce heat, so you can familiarize yourself with them so that you can recognize them correctly.
>
Tube boiler Fire-tube: The typical composition of a fire-tube boiler is:
Furnace: the water tank acts as a boiler
Chimney: there are tubes in the water tank that transfer the heat It transfers from the furnace and the chimney removes the heat and gases caused by the heating effect so that the pressure does not exceed the desired level. Therefore, the fuel is burned inside the furnace. The pipes transfer the heat of the furnace through the water inside the tank. When it is heated, the steam produced moves upward. Tube boilers are usually the cheapest type of boiler, as they are relatively simple in construction, but usually due to the thickness of the outer shell containing water, for Low to medium pressure applications are limited
Water tube boiler
This design is almost similar to the fire tube boiler, but instead of heating the furnace, it uses water tubes inside the furnace to heat the water in the tank. It heats. Likewise, a fuel source burns in the furnace and heats the water pipes inside. Again, when water is boiled, steam is produced and moves upward. Water tube boilers are more thermally efficient than fire tube boilers, but they are more complicated to construct and water quality can be a factor. be restrictive.

What type of fuel do steam boilers use?
Fire is the process of burning a fuel source. For a reaction to occur, there must be a source of fuel, heat, and an oxidizing agent. Boilers can be designed to burn a specific fuel, using any number of different technologies, but the main component that must be considered here is A fuel is a source of heat or fuel. Fuel is one of the most important aspects of a boiler and is what burns inside the boiler to produce heat. There are various sources that can be used.
Coal is the standard source of fuel. In industrial boiler applications, coal tends to be pulverized because it burns faster than traditional bricks. Electrical energy can be used as a heat source through resistance heating coils or electrode units. Electricity is usually used only for small commercial or domestic purposes.
Electrode applications require very high water quality and conductivity to function effectively. Maintenance is also key for electrode type applications, as cleaning is required to prevent arcing between the electrodes. Insulation is required. Gas boilers run on propane or natural gas, while oil boilers run on gasoline or liquid petroleum.
An example of the use of industrial boilers
There are different applications for which steam boilers are used.
They are used in the food industry. At different stages of production, food must be heated or boiled during processing. Steam boilers are widely used in domestic and industrial applications such as: - power plant. thermal processes
- industrial processes
- heating
- sanitation
- sterilization equipment
Corrosion is one of The main causes of boiler failure. Factors affecting the corrosion of steam boilers are: - high oxygen concentration - high temperature - high or low pH level >- Impurities in water
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Acidic corrosion
- Steam side burning (chemical reaction between pipe metal and steam)
- Fatigue cracking caused by repeated cyclical stress
The design, operation and maintenance of the boiler must comply with international safety standards and regulations to ensure reliability, safety, efficiency and prevent risks from boiler failure such as explosion. Corrosion prevention, effective monitoring and control are essential for boiler reliability. The control method is determined based on the type of corrosion. Common methods include maintaining proper pH, controlling oxygen, sediments and impurities, and reducing stress with proper design and operational methods.

